F5 Python SDK¶
The F5 Python SDK provides an interface to the iControl REST interface.
This provides the ability to translate actions that you would have normally done via the GUI to actions that can be performed from Python.
Via GUI
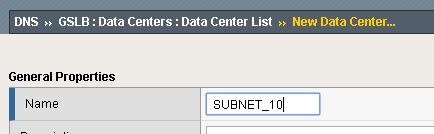
Via Code
def add_datacenter(self,datacenter):
"add datacenter in BIG-IP DNS"
self.mgmt.tm.gtm.datacenters.datacenter.create(name=datacenter,partition=self.partition)
This Lab will combine the process of creating a BIG-IP DNS deployment in Lab 2 and automate the process using the F5 Python SDK. The Python code in this lab is run as a script to deploy BIG-IP configurations. Think of this script like a remote tmsh Command Line Interface (CLI) to the BIG-IP. Here’s an example of adding a server to BIG-IP DNS using the script.
CLI example
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action add_datacenter --datacenter SUBNET_10
In this example we have created a Data Center (DC) named “SUBNET_10” using the F5 Python SDK example from before.
A full description of sample inputs (taken from this lab) can be found at the end of this lab in the Lab Appendix. The Script
For Python nerds; the pseudo code to invoke this from the CLI:
Python Pseudo Code
parser = OptionParser()
parser.add_option('--host')
parser.add_option('--datacenter')
parser.add_option('--action')
(options,args) = parser.parse_args()
dns_helper = DnsHelper(options.host)
if options.action == 'add_datacenter':
dns_helper.add_datacenter(options.datacenter)
Restoring the BIG-IP Configuration¶
This step is to cleanup the BIG-IP config that was created in Lab 2. RDP into the Windows jump host.
Reset both BIG-IP to be the same state as after Lab 1.
Find the “Resetting” links on the Desktop.

Double-click on both of these and you should see a window appear briefly like the following.
Verify that you no longer see the changes that were previously deployed.
Run Demo¶
This Lab is not intended to teach you how to write Python code, but instead demo how it can be leveraged to help automate a solution.
On the Desktop you will find the “Run Demo” link. Double-click the link.

The script is currently configured to output all the REST calls making for a verbose output.
An excerpt of the script that performs Lab 2 (create a DNS Sync Group):
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action enable_sync
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action add_datacenter --datacenter SUBNET_10
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action add_datacenter --datacenter SUBNET_30
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action add_server --datacenter SUBNET_10 --server_name bigip1 --server_ip=10.1.10.240
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action add_server --datacenter SUBNET_30 --server_name bigip2 --server_ip=10.1.30.240
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.7 \
--action save_config
sleep 3
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=10.1.1.8 \
--action gtm_add --peer_host=10.1.1.7 --peer_selfip 10.1.10.240
There is the same number of steps involved, but one-click!
The full script can be found on GitHub.
Exploring the Demo¶
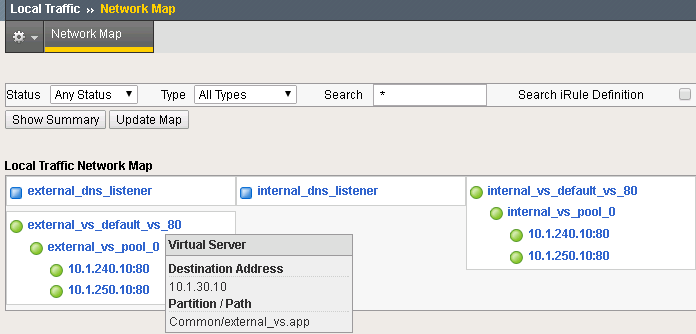
Take a look at what has been deployed. (Hint: Look at the Optional Exercise from Lab 2).
From the Network Map you can see that we have a set of external/internal DNS listeners and external/internal LTM Virtual Servers.
Application Services Integration iApp¶
The demo script utilizes the Application Services Integration iApp to deploy the LTM L4-L7 services.
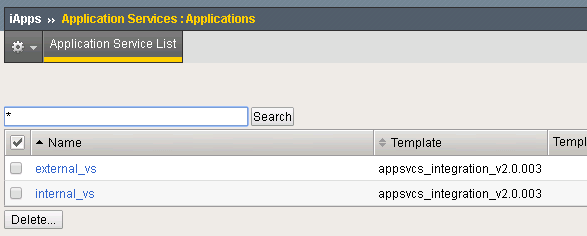
iApp Scripts
The iApp is deployed using modified scripts from: https://github.com/F5Networks/f5-application-services-integration-iApp/tree/master/scripts
# import Application Services Integration iApp onto BIG-IP
python iapps/import_template_bigip.py --impl iapps/iapp.tcl --apl iapps/iapp.apl 10.1.1.7 appsvcs_integration_v2.0.003
python iapps/import_template_bigip.py --impl iapps/iapp.tcl --apl iapps/iapp.apl 10.1.1.8 appsvcs_integration_v2.0.003
# Create L4-L7 services
python iapps/deploy_iapp_bigip.py -r 10.1.1.7 iapps/sample_http.json --strings pool__addr=10.1.10.10 \
--pool_members=0:10.1.240.10:80:0:1:10:enabled:none,0:10.1.250.10:80:0:1:0:enabled:none --iapp_name external_vs
python iapps/deploy_iapp_bigip.py -r 10.1.1.8 iapps/sample_http.json --strings pool__addr=10.1.30.10 \
--pool_members=0:10.1.250.10:80:0:1:10:enabled:none,0:10.1.240.10:80:0:1:0:enabled:none --iapp_name external_vs
python iapps/deploy_iapp_bigip.py -r 10.1.1.7 iapps/sample_http.json --strings pool__addr=10.1.10.100 \
--pool_members=0:10.1.240.10:80:0:1:10:enabled:none,0:10.1.250.10:80:0:1:0:enabled:none --iapp_name internal_vs
python iapps/deploy_iapp_bigip.py -r 10.1.1.8 iapps/sample_http.json --strings pool__addr=10.1.30.100 \
--pool_members=0:10.1.250.10:80:0:1:10:enabled:none,0:10.1.240.10:80:0:1:0:enabled:none --iapp_name internal_vs
You can view the parameters used to configure the iApp under iApps -> Application Services.
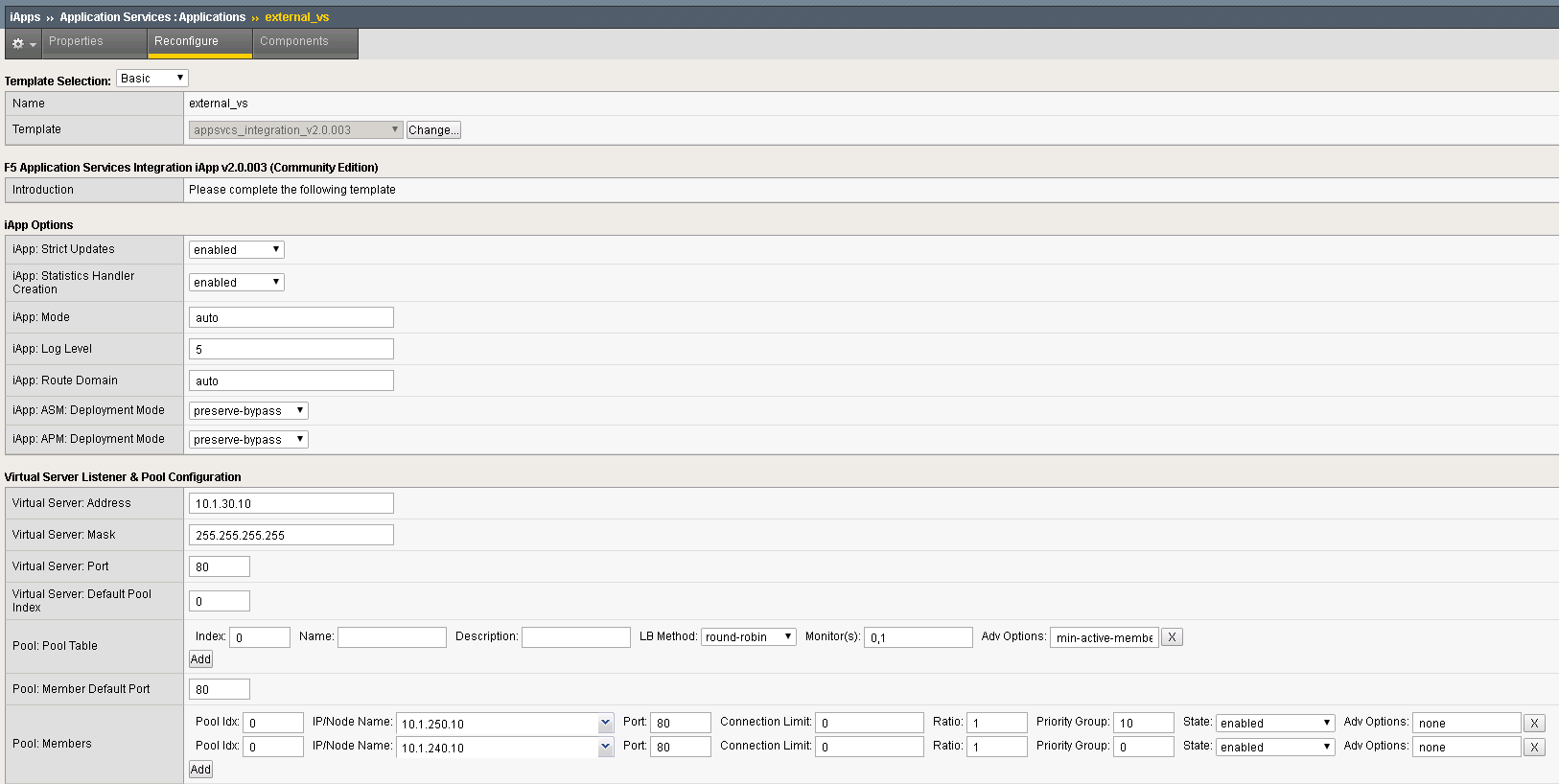
Testing Connections¶
This demo is designed to provide a solution with the following attributes.
- Two BIG-IP devices in separate Data Centers (Regions, Availability Zone, etc...)
- Two backend servers in separate DC
- The two DC are routable to each other via L3
- Provide recursive DNS for internal clients
The desired behavior for requests
- External clients round-robin between backend servers
- Persist External client requests to original DC server if requests move between DC
- Internal client requests will have affinity to local DC server
Testing External Connections¶
Find the “Test External” link.

Double-click on it and you should see:
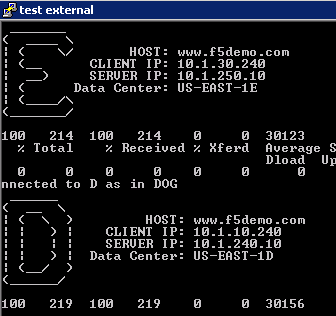
The “Test External” link is simulating requests from an external client. BIG-IP DNS is configured to use round-robin load balancing between the two backend servers.
From Google Chrome find the link for “www.f5demo.com”. The Windows Desktop client is configured to act like an external client.
Question Using Google Chrome the requests will always go back to the same server, why? (Hint: Look at the Optional Exercise from Lab 2).
Testing Internal Connections¶
Now run the “Test Server1” link.
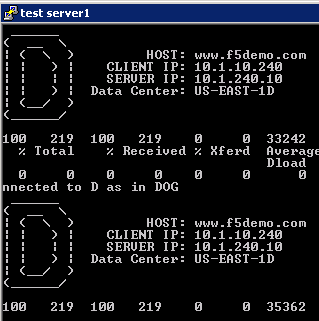
and run the “Test server2” link.
The “test-server[1-2]” links are simulating requests from internal clients. Note that BIG-IP DNS is configured to prefer requests to the same Data Center.
Question Can you explain how this is being done? (Hint: Look at the Optional Exercise from Lab 2).
Please proceed to Lab 4. Welcome to the Lab 4 Lab Guide
Optional Exercises¶
Changing the requirements¶
Can you change the behavior to the following:
- External requests will not persist to the same backend server (still round-robin, Hint: one change to each external LTM Virtual Server)
- Flip the affinity of the internal requests (could be done via either LTM/DNS)
Automating the change¶
The second change “flipping the affinity” can be done via changing the automation script to change how the LTM Virtual Servers are deployed. Reset the deployment and deploy with an updated deployment that implements that change.
Lab Appendix¶
The Python Script that is used in this lab was created by Eric Chen. This is considered F5 contributed software. K80012344 covers this.
From K80012344.
F5 contributed softwareF5 employees create and test software contributed to GitHub as part of supporting the development community related to F5 products. However, if the software is not a specific tagged release listed as F5 Supported in this article, and if the software is not also available on the F5 Downloads site, F5 does not provide technical support for them, and may refer you back to GitHub for community support for the project in question. For more information and for community discussions, refer to the information available for that software in the GitHub repository.
The Script¶
Enable DNS Sync¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action enable_sync
This performs the GUI steps of Enabling DNS Sync
Add Data Center¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action add_datacenter --datacenter [Data Center Name]
This performs the GUI steps of Add Data Center
Save Config¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action save_config
This performs the TMSH equivalent of:
save /sys config
save /sys config gtm-only
This ensures that the running configuration is saved to disk.
Syncing BIG-IP DNS¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP of BIG-IP that you will WIPE OUT DNS config] \
--action gtm_add
--peer_host=[MGMT IP of BIG-IP you want to copy from]
--peer_selfip [SELF IP of BIG-IP you want to copy from]
This performs the steps of Syncing BIG-IP DNS
Create DNS Cache¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action create_dns_cache
This performs the steps of DNS Cache
Create External DNS Profile¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] --action create_external_dns_profile
This performs the steps of External DNS Profile
Create Internal DNS Profile¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] --action create_internal_dns_profile
This performs the steps of Internal DNS Profile
Create External DNS Listener¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action create_external_dns_listener
--listener_ip [Listener IP]
This performs the steps of External DNS Listener
Create Internal DNS Listener¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action create_internal_dns_listener
--listener_ip [Listener IP]
--internal_network [Network/CIDR]
This performs the steps of Internal DNS Listener
Import iApp Template¶
python iapps/import_template_bigip.py --impl [TCL file] \
--apl [APL File] \
[MGMT IP] \
[Name of Template]
This will import the Application Services Integration iApp.
Deploy iApp¶
python iapps/deploy_iapp_bigip.py -r [MGMT IP] \
[JSON Input] \
--strings pool__addr=[Virtual Server IP] \
--pool_members=0:[Member IP]:[Member Port]:0:1:[Priority Group]:enabled:none,\
0:[Member IP]:[Member Port]:0:1:[Priority Group]:enabled:none
This will deploy an iApp. This is modified from the Application Services Integration iApp GitHub scripts to allow the specification of “strings” and “pool_members” from the CLI.
This performs the steps from LTM Configuration
Create DNS Virtual Server¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action create_vs \
--vip [LTM VS IP]:[LTM VS Port] \
--vip_translate [LTM VS External IP]:[LTM VS External Port]
--vs_name [DNS VS Name]
--server_name [Server Name (BIG-IP Device)]
This performs the steps from Step 1: Virtual Servers
Create DNS Pools¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action create_pool \
--name [Pool Name]
This performs the steps from Step 2: Pools. The pool is configured with a Topology LB method.
Create DNS Wide IP¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host=[MGMT IP] \
--action create_wideip \
--name [DNS Name] --pool [DNS Pool #1],[DNS Pool #2]
This performs the steps from Step 3: Wide IPs. The Wide IP is configured with a Topology LB method.
Create Topology Regions¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host [MGMT IP] \
--action create_region \
--name [Region Name] --internal_network [Subnet #1],[Subnet #2]
This performs the steps from Step 4: Topology Regions.
Create Topology Records¶
python bigip_dns_helper.py --host [MGMT IP]
--action create_topology_record
--name [Topology Record]
This performs the steps from Step 5: Topology Records. An example of a topology record: “ldns: region /Common/internal_network server: pool /Common/internal_pool”